Immunoadsorption Apheresis
Immune adsorption is particularly suitable for supporting the immune system in patients with autoimmune diseases in which the immune system attacks its own body cells. Immune adsorption is a method of therapeutic apheresis, i.e. it is used to remove pathogenic blood components. This procedure often leads to an improvement, especially if the pharmacologically active substances are no longer effective during drug therapy. In addition, immunoadsorption is a suitable therapy option if the disease was triggered by auto-antibodies from the IgG class.
Immunoadsorption is a direct procedure in which autoantibodies are quickly and effectively removed from the patient’s bloodstream. For this purpose, 2 Globaffin adsorbers – a synthetic broadband immune adsorber with peptide GAM-ligand – are used. Above all, this efficiently removes immunoglobulins (IgG) and immune complexes. The plasma continuously obtained in this way, using a cell separator, is passed through one of the two double adsorbers (GLOBAFFIN®) for immune adsorption and is thus freed of antibodies and immune complexes. The treated plasma is combined with the blood and reinfused into the patient.
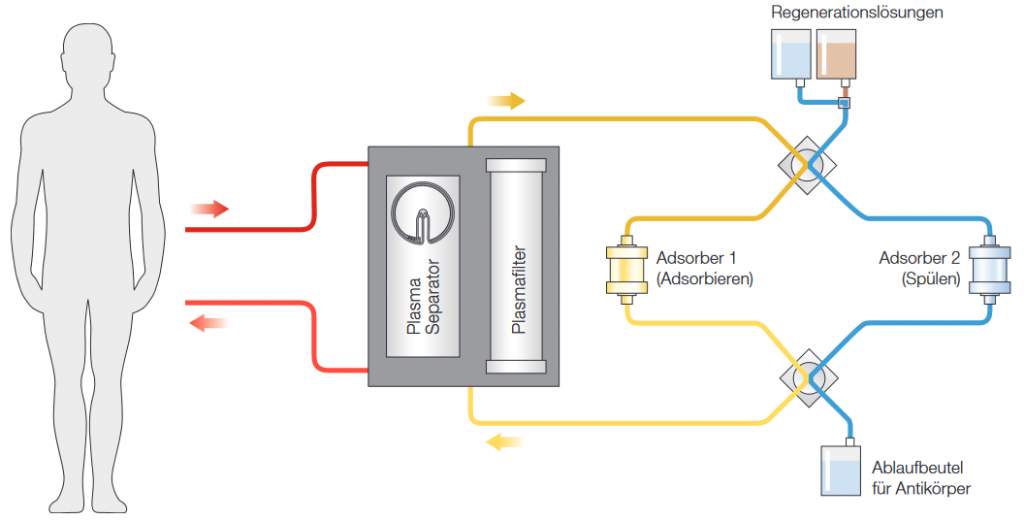
Since essential plasma components remain largely unaffected due to the selectivity of the immunoadsorption, large plasma volumes can be treated.

IgG adsorbers are used in chronic forms of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, such as:
Chronisch inflammatorische demyelinisierende Polyneuropathie (CIDP) Rheumatoide Arthritis
- Long Covid Syndrome
- Post Vaccine Syndromes
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Myasthenia gravis
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- multiple sclerosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Wegener’s disease
Equally good results have been recorded for many other indications, such as:
- fatigue
- exercise-related shortness of breath
- cognitive disorders
- sleep disorders
- Headache
- muscle pain (myalgia)
- neuropathies

